MTM in Long Term Care
Overview
Pharmacists who work in or support patients living in long-term care (LTC) facilities or other institutional environments play a vital role in patient health. In these unique settings, the range of covered services available may be limited, and this resource can be used to determine which services are appropriate to provide for the patient. These guidelines serve as minimum requirements for conditions for service provision – pharmacists must use professional judgement beyond these guidelines to ensure the service is appropriate. Note: in the Outcomes platform service documentation workflows, consider the use of the word “patient” to also include authorized representative in cases where the patient resides in these settings.
Covered Services - TIPs (Targeted Interventions)
Eligible patients who reside in long-term care or other types of institutional living settings have additional considerations when determining the eligible recipient for certain covered services. Understanding if the patient is cognitively intact and who is responsible for administering the patient’s medications will help determine which services can be provided for the patient and which recipients are allowable. TIPs can be grouped as either patient consultations or prescriber consultations depending on the requirements of the service.
Prescriber Consultations
Prescriber consultation TIP types can be completed by coordinating with the prescriber and involving the patient and/or another authorized representative (i.e. healthcare staff or caregiver) when appropriate in the LTC setting. A patient that manages their own medications and/or is cognitively intact would be expected to be more involved in a service requiring a therapy change.
-
TIP types that are considered prescriber consultations include:
-
Cost-effective Alternative
-
Drug Interaction
-
Needs Drug Therapy
-
Suboptimal Drug
-
Patient Consultations
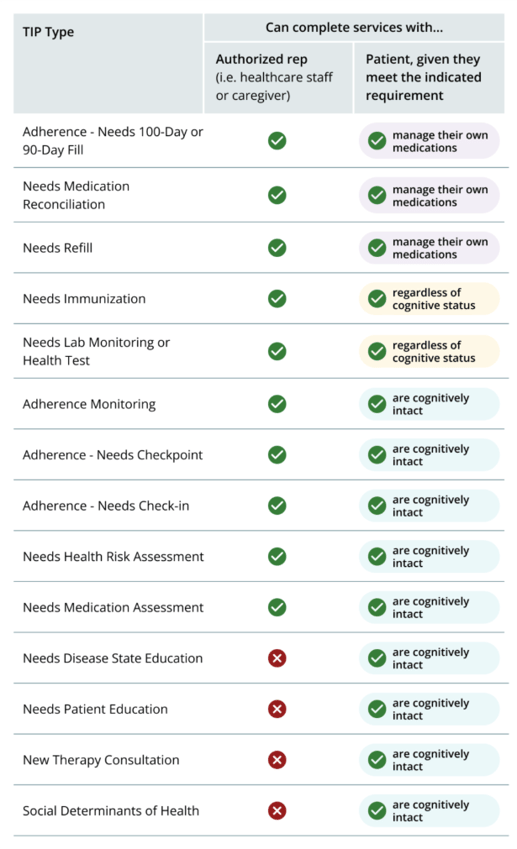
Many patient consultation TIP types can be completed either with an authorized representative (i.e. healthcare staff or caregiver) or the patient under certain conditions in the LTC setting. Patient consultation TIPs require consultation with the patient or authorized representative at a minimum but may require prescriber consultation as well.
- TIP types that can be completed with an authorized representative OR patient if cognitively intact:
- Adherence Monitoring
-
- Adherence – Needs Checkpoint
-
- Adherence – Needs Check-in
-
- Needs Health Risk Assessment
-
- Needs Medication Assessment
- TIP types that can be completed with an authorized representative OR patient if patient manages their own meds:
-
- Adherence - Needs 100-day or 90-Day Fill, Adherence - Needs 100-day Fill, Adherence - Needs 90-day Fill
-
- Needs Medication Reconciliation
-
- Needs Refill
- TIP types that can be completed in coordination with an authorized representative and patient, regardless of cognitive status.
-
- Needs Immunization
-
- Needs Lab Monitoring or Health Test
Patient consultation TIP types that are education based can only be completed with the patient, if the patient is cognitively intact. These TIPs cannot be completed with an authorized representative.
- TIP types that can only be completed with a patient who is cognitively intact:
-
- Needs Disease State Education
-
- Needs Patient Education
-
- New Therapy Consultation
- Social Determinants of Health
Patient Consultations TIP Summary
Comprehensive Medication Reviews in Long-Term Care
Outcomes and CMS expect CMRs in the LTC setting to meet the following professional service definition:
Interactive, person-to-person and real-time between the patient and the pharmacist or with another authorized individual and the pharmacist when the patient has been identified as cognitively impaired.
Delivering CMRs in LTC
Who can provide the CMR?
- Pharmacist at the pharmacy that is dispensing the patients' medications
- Consultant pharmacist affiliated with the dispensing pharmacy that conducts medication regimen reviews for the facility
- Pharmacists embedded within physician clinics or health systems
Who can receive the CMR?
- If the patient is cognitively intact, conduct the CMR with the patient. The CMR may also be completed with the patient and someone else if that is the patient’s preference.
- If the patient is cognitively impaired, conduct the CMR with an authorized representative. Authorized representatives include:
- Prescriber
- Legally authorized representative - caregiver
- Legally authorized representative - other individual
- Document if cognitive impairment was determined by testing at the facility (BIMS, MMSE), documentation in patient chart or confirmation with healthcare staff or family member.
Who should I contact?
- The patient, if possible
- Ask to speak to the nurse who takes care of the patient. Other potentially appropriate facility nursing staff for CMR offer and/or delivery include:
- DON (Director of Nursing)
- MDS (Minimum Data Set) Coordinator/Nurse
- ADON (Assistant Director of Nursing)
- Unit Manager/Charge Nurse
- Floor Nurse
Monthly Medication Regimen Review (MRR) vs. Comprehensive Medication Review (CMR)
Sometimes the CMR can be confused with the Medication Regimen Review (MRR) in LTC, but these are two separate services that may be completed by the same or different providers.
| CMR | MRR |
| Interactive | Chart review |
| Patient eligible based on medications and conditions | Required for all skilled nursing facility (SNF) residents |
| Assess whole regimen (cost, side effects, drug therapy problems) | Focus on clinical problems and compliance |
| Yearly review | Monthly review |
Best Practices
- If the CMR needs to be completed with nursing staff, offer to schedule a time, especially if there are multiple CMR-eligible patients at the facility.
- Prior to calling the facility or patient, verify the CMR can be delivered by phone by checking the Outcomes platform.
- Check with facility nursing staff to see if prescriber recommendations can be faxed to the facility for the prescriber to review. Fax the recommendation with attention to the patient's caregiver or the staff member who was the CMR recipient, if applicable.